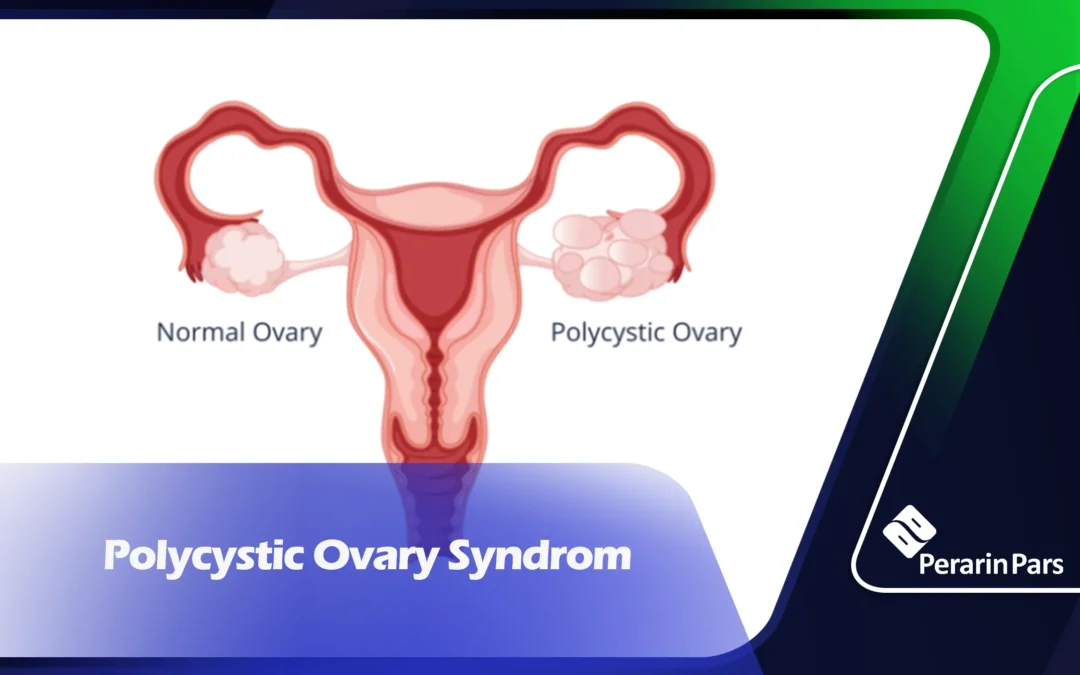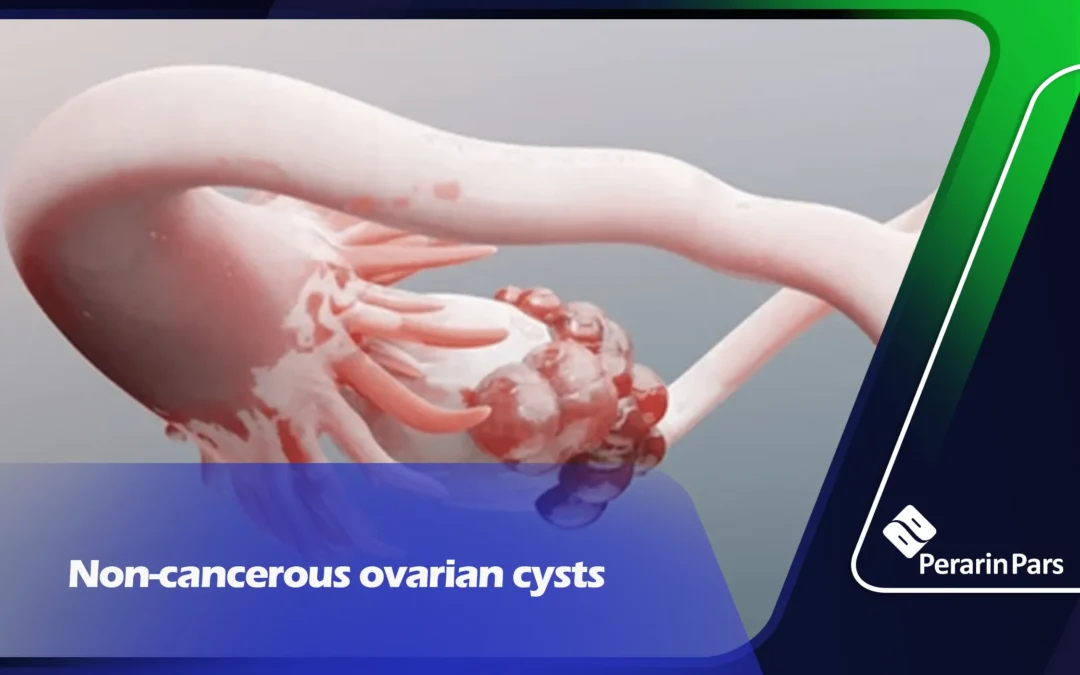
Non-cancerous ovarian cysts
by Website Writer | بهمن 10, 1401 | Articles
Non-cancerous ovarian cysts are classified into types including:
- Follicular cysts
- Corpus luteum cysts
- Hemorrhagic cysts
- Dermoid cysts
Factors such as age, race, family history, and genetic predisposition play significant roles in the development of non-cancerous ovarian cysts. Many studies have shown the influence of genetic factors on female reproductive system disorders. However, other research indicates that:
Family history accounts for only 4-5% of ovarian abnormalities.
Therefore, environmental factors and lifestyle play a more crucial role in ovarian abnormalities, including:
- Hypothyroidism
- Hormonal imbalances
- Ovarian cancer
- Breast cancer
- Follicular dysfunction
Among these, hypothyroidism is one of the most significant conditions that can lead to ovarian cyst formation. Diabetes is also associated with ovarian cysts. Some studies suggest a link between thalassemia and ovarian cysts. Additionally, stress and anxiety are prominent factors contributing to ovarian cyst development. Some studies have shown a meaningful connection between blood types and benign tumors of the uterus and ovaries.
Conclusion: The relationship between blood type phenotypes and the development of ovarian cysts is a topic for further investigation. Additionally, many studies highlight the connection between a wide range of diseases and dietary habits. Therefore:
Reducing psychological stress, Managing anxiety, Maintaining a proper diet,
Can play a significant role in preventing ovarian cysts. Moreover, supplements such as IP-6 (Inositol hexaphosphate) can greatly assist in improving conditions for women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).